Ingot - Foundry Marine Engineering: A Deep Dive into Induction Melting Furnaces
Formerly recognized as Feilding's Foundry, Ingot is a renowned name in the foundry marine engineering realm. With a commitment to exceptional quality and pioneering technology, the foundry has carved a niche for itself, especially with its sophisticated induction melting furnaces. This article delves deep into the workings and benefits of these furnaces, and the various metals Ingot works with.
Understanding Induction Furnaces
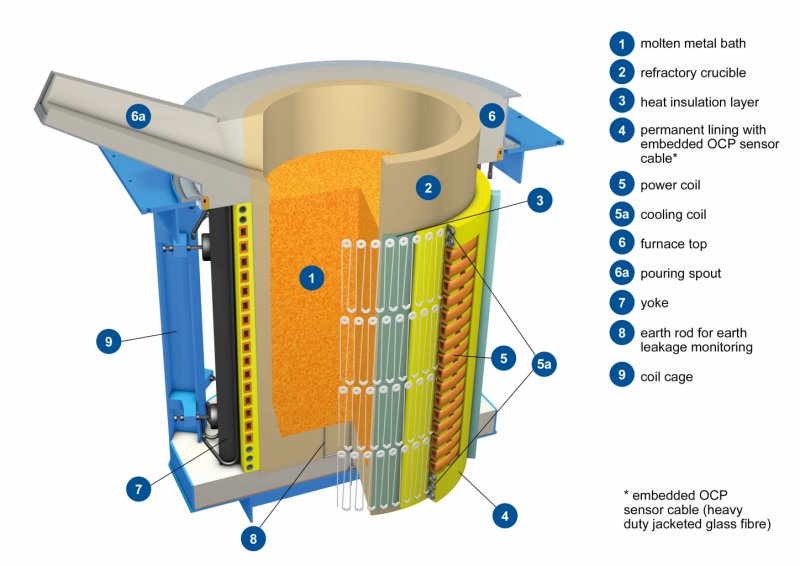
An induction furnace is an electric furnace in which metal gets melted by electromagnetic induction. But how does it work?
How an Induction Furnace Works
Electromagnetic Induction: When an AC current passes through a coil, it generates a magnetic field around it. When a metal is placed inside this coil, the magnetic field induces electric currents (eddy currents) within the metal.
Joule Heating: These induced eddy currents generate heat through resistance (Joule Heating). This heat effectively melts the metal inside the furnace.
Crucible: The furnace utilizes a refractory-lined crucible to hold the metal, ensuring it remains in pristine condition.
Advantages of Induction Melting Furnace
Energy Efficiency: Induction furnaces often require less energy than traditional furnaces, making them cost-effective.
Speed: The melting process in induction furnaces is significantly faster, ensuring rapid production cycles.
Uniform Heating: The even distribution of electromagnetic waves ensures consistent heating and reduces the risk of hot spots.
Flexibility: They are versatile and can handle a variety of metals, as evidenced by Ingot's foundry.
Cleaner Process: Reduced combustion results in fewer impurities and emissions, making it an environmentally friendly option.
Ingot's Rich Palette of Metals
The flexibility of Ingot's induction furnaces is demonstrated by its impressive range of non-ferrous metals:
CMA1: A popular choice for its excellent corrosion resistance.
AB2: Widely used for its high tensile strength.
Aluminium: Known for its lightweight and resistance to corrosion.
LG2: Esteemed for its superior casting properties.
From Feilding's Foundry to Ingot
By rebranding from Feilding's Foundry to Ingot, the company has unified its vision and branding, ensuring that clients recognise the quality and expertise they've come to expect, irrespective of the project's nature.
For a deeper understanding and to explore the fascinating world of Ingot's foundry marine engineering, their official website offers an expansive resource.
#IngotFoundry #MarineEngineering #InductionFurnace #FoundryTechnology #IngotMetals


Comments